Update documentation for v4 |
||
|---|---|---|
| .devcontainer | ||
| .github | ||
| .licenses/npm | ||
| __tests__ | ||
| dist | ||
| src | ||
| .eslintignore | ||
| .eslintrc.json | ||
| .gitattributes | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .licensed.yml | ||
| .prettierignore | ||
| .prettierrc.json | ||
| CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md | ||
| CONTRIBUTING.md | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
| action.yml | ||
| jest.config.js | ||
| package-lock.json | ||
| package.json | ||
| tsconfig.json | ||
README.md
@actions/upload-artifact
Upload Actions Artifacts from your Workflow Runs. Internally powered by @actions/artifact package.
See also download-artifact.
@actions/upload-artifact- v4 - What's new
- Usage
- Examples
- Upload an Individual File
- Upload an Entire Directory
- Upload using a Wildcard Pattern
- Upload using Multiple Paths and Exclusions
- Altering compressions level (speed v. size)
- Customization if no files are found
- (Not) Uploading to the same artifact
- Environment Variables and Tilde Expansion
- Retention Period
- Using Outputs
- Limitations
- Where does the upload go?
v4 - What's new
[!IMPORTANT] upload-artifact@v4+ is not currently supported on GHES yet. If you are on GHES, you must use v3.
The release of upload-artifact@v4 and download-artifact@v4 are major changes to the backend architecture of Artifacts. They have numerous performance and behavioral improvements.
For more information, see the @actions/artifact documentation.
Improvements
- Uploads are significantly faster, upwards of 90% improvement in worst case scenarios.
- Once uploaded, an Artifact ID is returned and Artifacts are immediately available in the UI and REST API. Previously, you would have to wait for the run to be completed before an ID was available or any APIs could be utilized.
- The contents of an Artifact are uploaded together into an immutable archive. They cannot be altered by subsequent jobs. Both of these factors help reduce the possibility of accidentally corrupting Artifact files.
- The compression level of an Artifact can be manually tweaked for speed or size reduction.
Breaking Changes
-
On self hosted runners, additional firewall rules may be required.
-
Uploading to the same named Artifact multiple times.
Due to how Artifacts are created in this new version, it is no longer possible to upload to the same named Artifact multiple times. You must either split the uploads into multiple Artifacts with different names, or only upload once. Otherwise you will encounter an error.
-
Limit of Artifacts for an individual job. Each job in a workflow run now has a limit of 10 artifacts.
Usage
Inputs
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
# Name of the artifact to upload.
# Optional. Default is 'artifact'
name:
# A file, directory or wildcard pattern that describes what to upload
# Required.
path:
# The desired behavior if no files are found using the provided path.
# Available Options:
# warn: Output a warning but do not fail the action
# error: Fail the action with an error message
# ignore: Do not output any warnings or errors, the action does not fail
# Optional. Default is 'warn'
if-no-files-found:
# Duration after which artifact will expire in days. 0 means using default retention.
# Minimum 1 day.
# Maximum 90 days unless changed from the repository settings page.
# Optional. Defaults to repository settings.
retention-days:
# The level of compression for Zlib to be applied to the artifact archive.
# The value can range from 0 to 9.
# For large files that are not easily compressed, a value of 0 is recommended for significantly faster uploads.
# Optional. Default is '6'
compression-level:
Outputs
| Name | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
artifact-id |
GitHub ID of an Artifact, can be used by the REST API | 1234 |
Examples
Upload an Individual File
steps:
- run: mkdir -p path/to/artifact
- run: echo hello > path/to/artifact/world.txt
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: my-artifact
path: path/to/artifact/world.txt
Upload an Entire Directory
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: my-artifact
path: path/to/artifact/ # or path/to/artifact
Upload using a Wildcard Pattern
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: my-artifact
path: path/**/[abc]rtifac?/*
Upload using Multiple Paths and Exclusions
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: my-artifact
path: |
path/output/bin/
path/output/test-results
!path/**/*.tmp
For supported wildcards along with behavior and documentation, see @actions/glob which is used internally to search for files.
If a wildcard pattern is used, the path hierarchy will be preserved after the first wildcard pattern:
path/to/*/directory/foo?.txt =>
∟ path/to/some/directory/foo1.txt
∟ path/to/some/directory/foo2.txt
∟ path/to/other/directory/foo1.txt
would be flattened and uploaded as =>
∟ some/directory/foo1.txt
∟ some/directory/foo2.txt
∟ other/directory/foo1.txt
If multiple paths are provided as input, the least common ancestor of all the search paths will be used as the root directory of the artifact. Exclude paths do not affect the directory structure.
Relative and absolute file paths are both allowed. Relative paths are rooted against the current working directory. Paths that begin with a wildcard character should be quoted to avoid being interpreted as YAML aliases.
Altering compressions level (speed v. size)
If you are uploading large or easily compressable data to your artifact, you may benefit from tweaking the compression level. By default, the compression level is 6, the same as GNU Gzip.
The value can range from 0 to 9:
- 0: No compression
- 1: Best speed
- 6: Default compression (same as GNU Gzip)
- 9: Best compression
Higher levels will result in better compression, but will take longer to complete.
For large files that are not easily compressed, a value of 0 is recommended for significantly faster uploads.
For instance, if you are uploading random binary data, you can save a lot of time by opting out of compression completely, since it won't benefit:
- name: Make a 1GB random binary file
run: |
dd if=/dev/urandom of=my-1gb-file bs=1M count=1000
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: my-artifact
path: my-1gb-file
compression-level: 0 # no compression
But, if you are uploading data that is easily compressed (like plaintext, code, etc) you can save space and cost by having a higher compression level. But this will be heavier on the CPU therefore slower to upload:
- name: Make a file with a lot of repeated text
run: |
for i in {1..100000}; do echo -n 'foobar' >> foobar.txt; done
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: my-artifact
path: foobar.txt
compression-level: 9 # maximum compression
Customization if no files are found
If a path (or paths), result in no files being found for the artifact, the action will succeed but print out a warning. In certain scenarios it may be desirable to fail the action or suppress the warning. The if-no-files-found option allows you to customize the behavior of the action if no files are found:
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: my-artifact
path: path/to/artifact/
if-no-files-found: error # 'warn' or 'ignore' are also available, defaults to `warn`
(Not) Uploading to the same artifact
Unlike earlier versions of upload-artifact, uploading to the same artifact via multiple jobs is not supported with v4.
- run: echo hi > world.txt
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
# implicitly named as 'artifact'
path: world.txt
- run: echo howdy > extra-file.txt
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
# also implicitly named as 'artifact', will fail here!
path: extra-file.txt
Artifact names must be unique since each created artifact is idempotent so multiple jobs cannot modify the same artifact.
In matrix scenarios, be careful to not accidentally upload to the same artifact, or else you will encounter conflict errors. It would be best to name the artifact with a prefix or suffix from the matrix:
jobs:
upload:
name: Generate Build Artifacts
strategy:
matrix:
os: [ubuntu-latest, windows-latest]
version: [a, b, c]
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
steps:
- name: Build
run: ./some-script --version=${{ matrix.version }} > my-binary
- name: Upload
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: binary-${{ matrix.os }}-${{ matrix.version }}
path: my-binary
This will result in artifacts like: binary-ubuntu-latest-a, binary-windows-latest-b, and so on.
Previously the behavior allowed for the artifact names to be the same which resulted in unexpected mutations and accidental corruption. Artifacts created by upload-artifact@v4 are immutable.
Environment Variables and Tilde Expansion
You can use ~ in the path input as a substitute for $HOME. Basic tilde expansion is supported:
- run: |
mkdir -p ~/new/artifact
echo hello > ~/new/artifact/world.txt
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: Artifacts-V4-beta
path: ~/new/**/*
Environment variables along with context expressions can also be used for input. For documentation see context and expression syntax:
env:
name: my-artifact
steps:
- run: |
mkdir -p ${{ github.workspace }}/artifact
echo hello > ${{ github.workspace }}/artifact/world.txt
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: ${{ env.name }}-name
path: ${{ github.workspace }}/artifact/**/*
For environment variables created in other steps, make sure to use the env expression syntax
steps:
- run: |
mkdir testing
echo "This is a file to upload" > testing/file.txt
echo "artifactPath=testing/file.txt" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: artifact
path: ${{ env.artifactPath }} # this will resolve to testing/file.txt at runtime
Retention Period
Artifacts are retained for 90 days by default. You can specify a shorter retention period using the retention-days input:
- name: Create a file
run: echo "I won't live long" > my_file.txt
- name: Upload Artifact
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: my-artifact
path: my_file.txt
retention-days: 5
The retention period must be between 1 and 90 inclusive. For more information see artifact and log retention policies.
Using Outputs
If an artifact upload is successful then an artifact-id output is available. This ID is a unique identifier that can be used with Artifact REST APIs.
Example output between steps
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
id: artifact-upload-step
with:
name: my-artifact
path: path/to/artifact/content/
- name: Output artifact ID
run: echo 'Artifact ID is ${{ steps.artifact-upload-step.outputs.artifact-id }}'
Example output between jobs
jobs:
job1:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
outputs:
output1: ${{ steps.my-artifact.outputs.artifact-id }}
steps:
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
id: artifact-upload-step
with:
name: my-artifact
path: path/to/artifact/content/
job2:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
needs: job1
steps:
- env:
OUTPUT1: ${{needs.job1.outputs.output1}}
run: echo "Artifact ID from previous job is $OUTPUT1"
Limitations
Number of Artifacts
Within an individual job, there is a limit of 10 artifacts that can be created for that job.
You may also be limited by Artifacts if you have exceeded your shared storage quota. Storage is calculated every 6-12 hours. See the documentation for more info.
Zip archives
When an Artifact is uploaded, all the files are assembled into an immutable Zip archive. There is currently no way to download artifacts in a format other than a Zip or to download individual artifact contents.
Permission Loss
File permissions are not maintained during artifact upload. All directories will have 755 and all files will have 644. For example, if you make a file executable using chmod and then upload that file, post-download the file is no longer guaranteed to be set as an executable.
If you must preserve permissions, you can tar all of your files together before artifact upload. Post download, the tar file will maintain file permissions and case sensitivity.
- name: 'Tar files'
run: tar -cvf my_files.tar /path/to/my/directory
- name: 'Upload Artifact'
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: my-artifact
path: my_files.tar
Where does the upload go?
At the bottom of the workflow summary page, there is a dedicated section for artifacts. Here's a screenshot of something you might see:
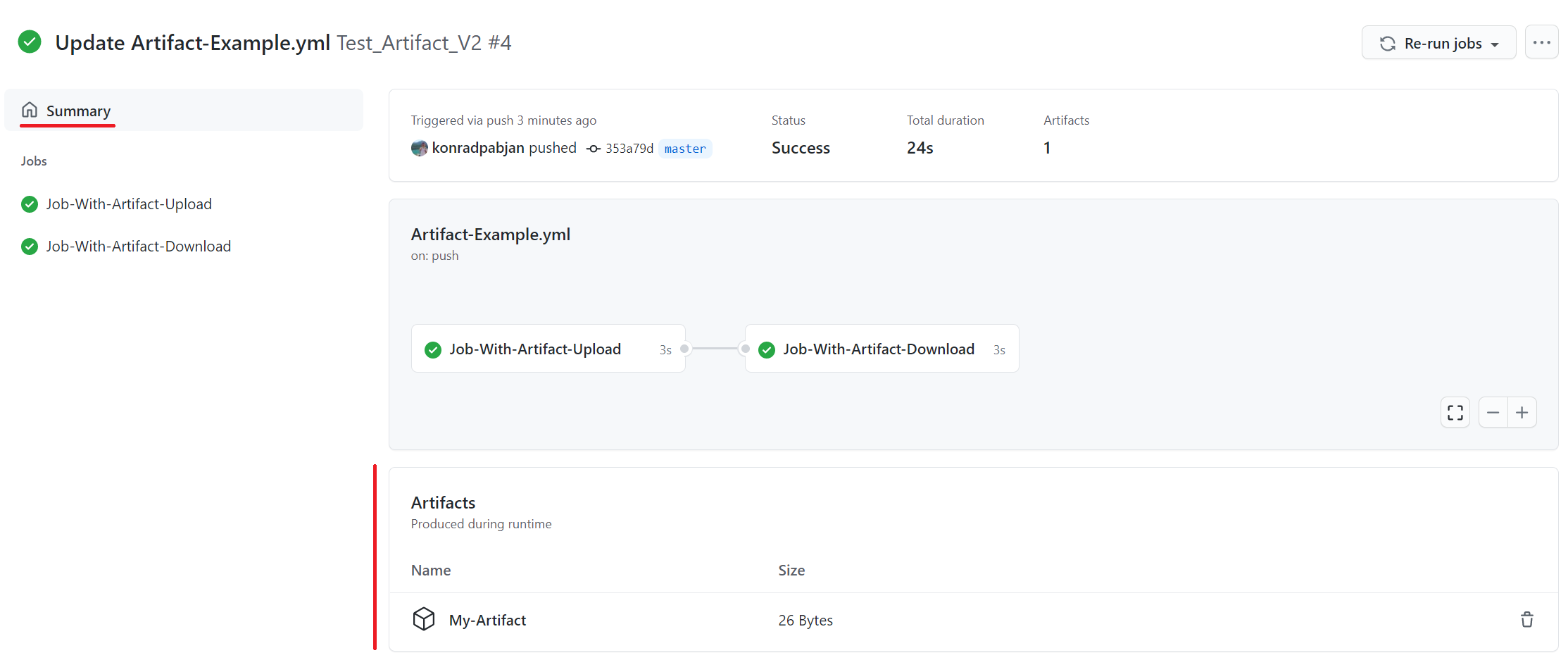
There is a trashcan icon that can be used to delete the artifact. This icon will only appear for users who have write permissions to the repository.
The size of the artifact is denoted in bytes. The displayed artifact size denotes the size of the zip that upload-artifact creates during upload.